Have you ever felt a sharp pain in your back that just won’t go away? Have you ever wondered if you might have a herniated disc? If so, don’t worry, in today’s article we are going to solve all the doubts that may arise in the face of such discomfort.
The herniated disc is a common condition that affects many people, causing significant pain and discomfort and, in many cases, affecting their quality of life, as it often affects mobility in the lower back. lumbar region. So, knowing the symptoms, treatment options and preventive measures can help you make informed decisions about your health.
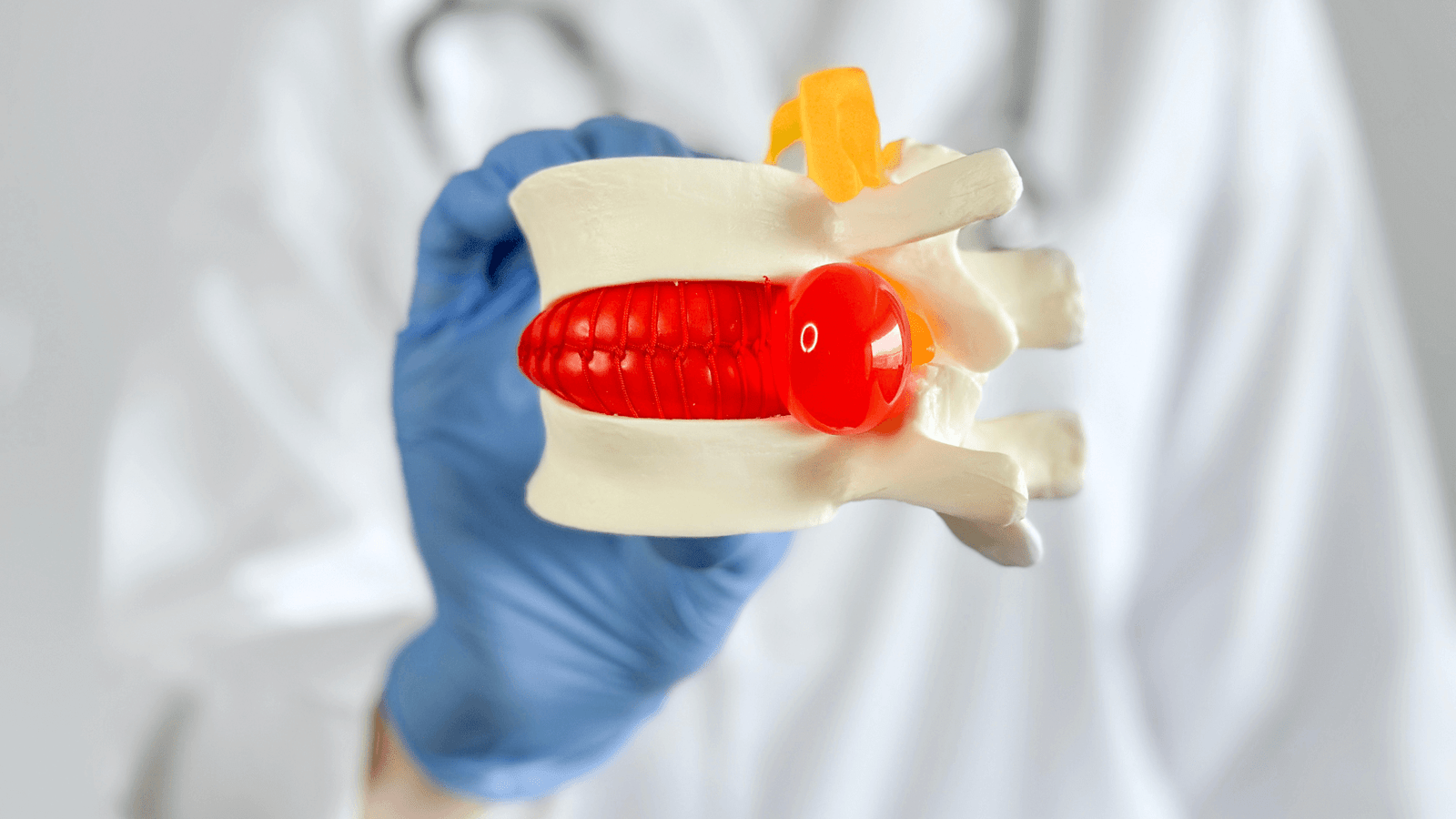
What is disc herniation?
The herniated disc is a condition that occurs when one of the intervertebral discs intervertebral discswhich act as cartilaginous cushions (i.e., cushions) for the vertebrae of the spine, slips out of its normal position and presses on the surrounding nerves.
For their part, the intervertebral discs are soft, gelatinous structures surrounded by a tougher fibrous ring. Their main function is to absorb impact and allow flexibility of the spine, facilitating movements such as bending, twisting and lifting.
When one of these discs becomes damaged or degenerates, it can slip out of place, a phenomenon known as “protrusion” or “disc slippage”.protrusion” or “disc displacement“. This displacement can occur in any part of the spine, but is more common in the cervical region (neck) and in the lumbar region (lower back), where mobility and load on the spine are greater.
This displacement may cause severe pain and/or weakness in the extremities.
What are the most common symptoms?
Identifying the symptoms of a herniated disc is crucial to getting proper treatment. Symptoms can vary depending on the location and severity of the herniation, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Pain especially in the lower back or neck, which may radiate into the legs (sciatica) or arms (brachialgia)
- Muscle weakness which causes loss of strength in the affected muscles, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
- Numbness or tingling sensation in the extremities, which may extend along the path of the affected nerve.which may extend along the path of the affected nerve.
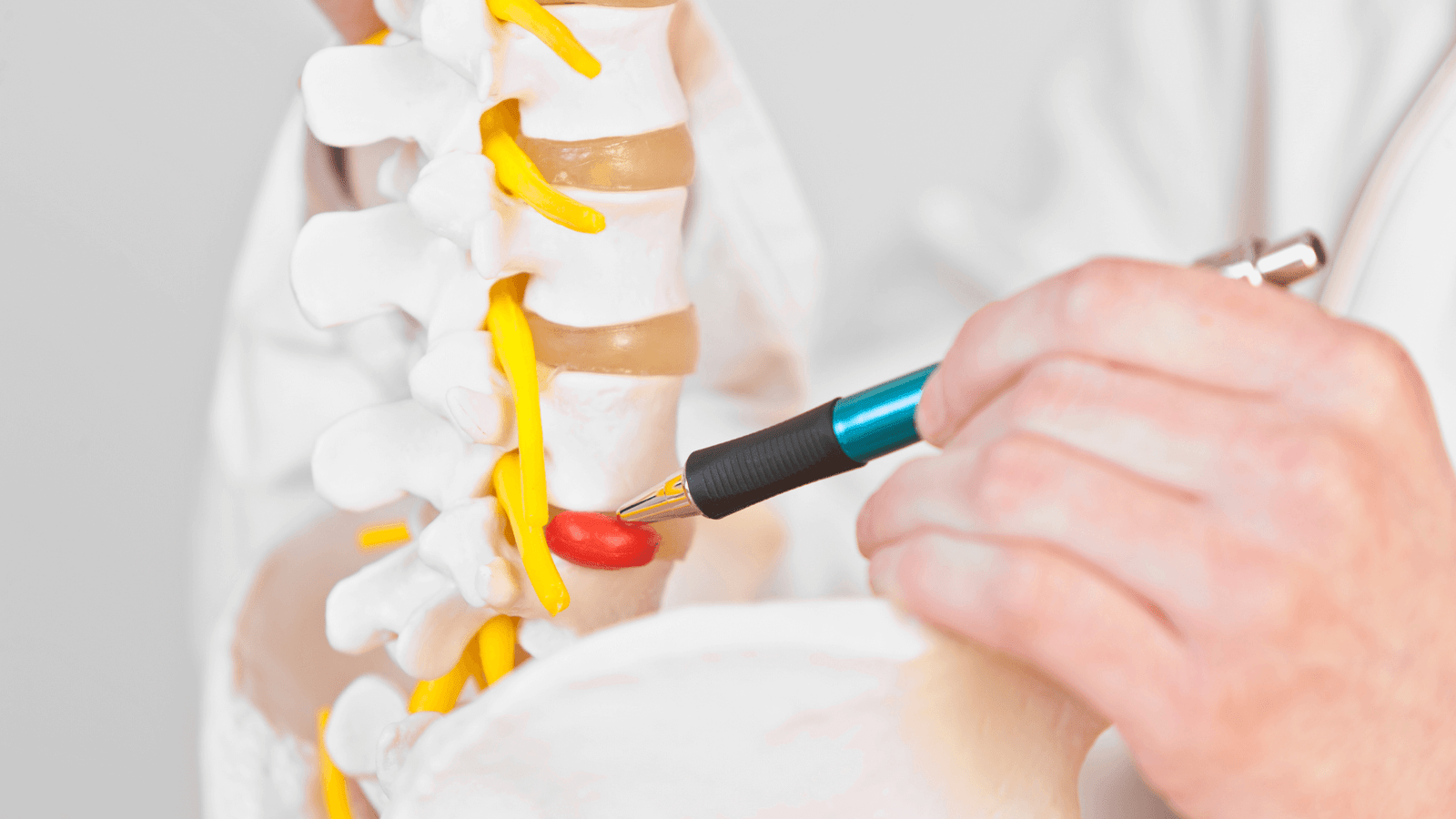
Which regions are affected?
- Lumbar region: lumbar disc herniation is the most common and usually affects the lower segments of the spine. Pain may radiate from the lower back to the legs, a condition known as sciatica.
- Cervical region: cervical disc herniation affects the vertebrae in the neck, causing pain that may radiate to the shoulders and arms.
Thoracic region: although less common, a herniated disc in the thoracic region (middle of the back) can also occur, causing pain in the middle of the back, radiating to the thorax.
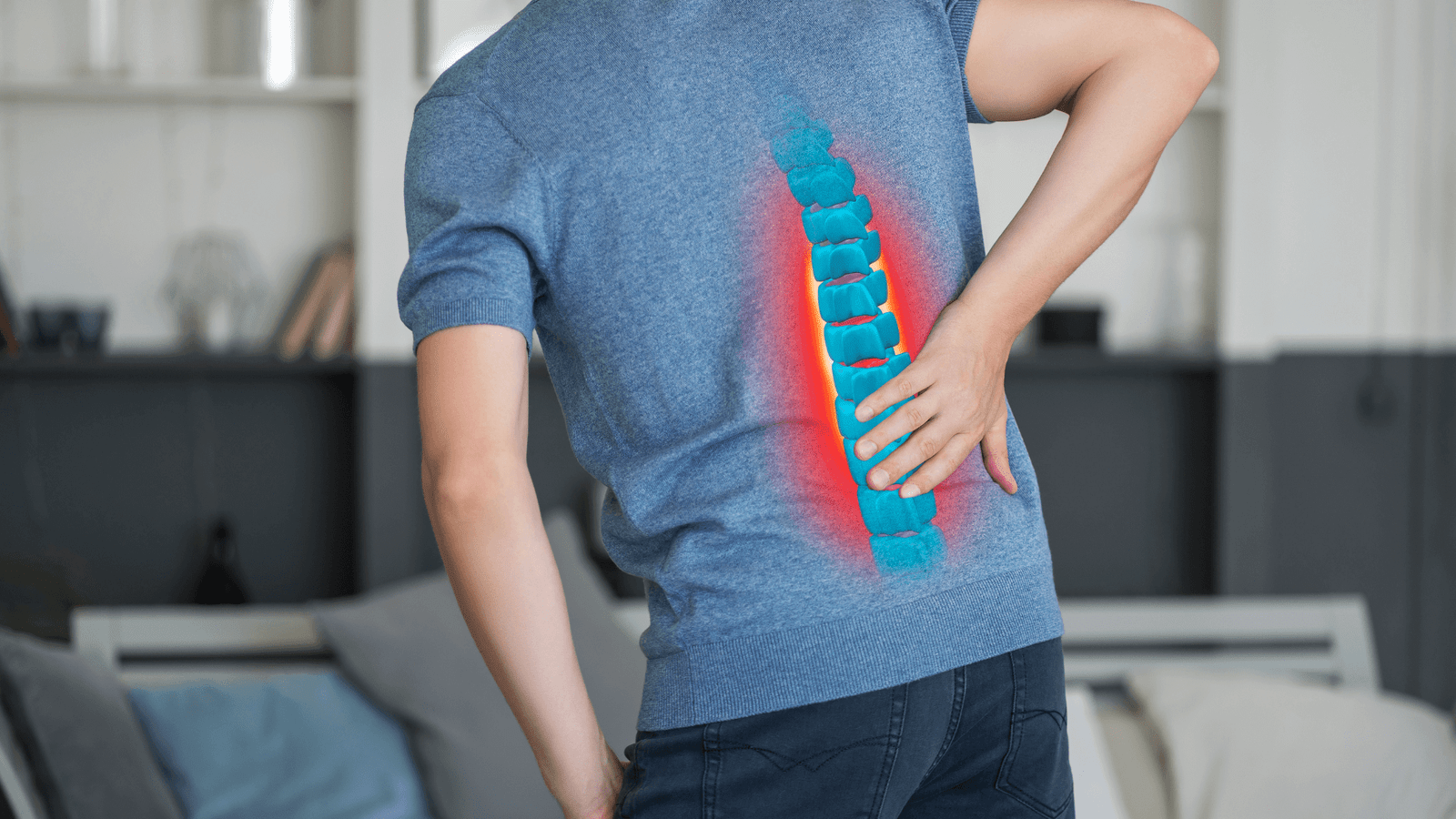
Causes and risk factors
The causes of disc herniation can vary, but some common risk factors include:
- Disc degeneration: with aging, intervertebral discs can lose their water content, becoming less flexible and more prone to damage.
- InjuriesInjuries: a trauma such as a simple fall in the street, at home or an excessive physical effort such as weight lifting, sometimes generates the displacement of a disc.
- LifestyleLifestyle: factors such as overweight, sedentary lifestyle and improper lifting of heavy objects can increase the risk of developing a herniated disc.
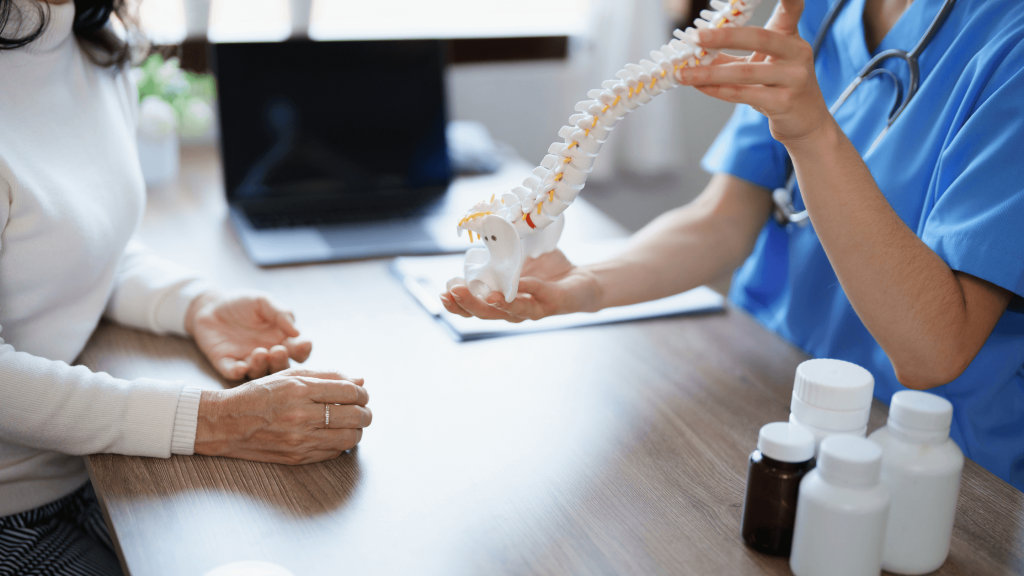
Diagnosis of disc herniation
Accurate diagnosis of a herniated disc is essential to develop an effective and personalized treatment plan.
The first step in the diagnosis of a herniated disc is usually a complete physical exam complete physical examination. During this evaluation, the physician will perform several tests to verify:
- ReflexesReflexes: evaluation of reflexes to detect any change in the neurological response that may indicate nerve compression.
- Muscle strengthMuscle strength testing of the extremities to identify muscle weakness that may be associated with nerve compression.
- SensitivitySensitivity: evaluation of sensitivity to detect areas of numbness or pain corresponding to the affected nerves.
To confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity severity of the herniated disccomplementary tests are used, such as:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): this imaging technique is extremely useful for visualizing the intervertebral discs and surrounding nerves, providing a clear and detailed image of the spine.
- Electromyogram (EMG): when you want to identify which is the affected root in cases of multisegmental involvement.
In short, medical examination is a key step in the management of persistent back pain.. An accurate diagnosis not only helps to confirm the presence of a herniated disc, but also rules out other possible causes of low back pain.
If you experience persistent symptoms of back pain or sciatica, it is critical to seek a professional medical evaluation. The combination of a detailed physical examination and complementary testing allows neurosurgeons to accurately diagnose the herniated disc and plan the most appropriate treatment. Don’t underestimate the importance of a medical check-up; your long-term health and well-being depend on timely diagnosis and treatment.

Minimally invasive disc herniation surgery.
Minimally invasive disc herniation surgery has revolutionized the treatment of this condition, offering patients a safer and less invasive option for pain relief. This advanced approach is distinguished by its precise techniques, less surgical trauma and significantly reduced recovery times.
The minimally invasive surgery for herniated discs involves the use of small incisions and specialized tools to access and repair the affected disc. Unlike traditional surgery, which requires large incisions and extensive displacement of surrounding tissues, this technique allows the surgeon to treat the herniated disc with greater precision and less collateral damage..
Opt for minimally invasive minimally invasive surgery for the treatment of a herniated disc offers multiple benefits, including:
- Less postoperative pain: smaller incisions and less tissue manipulation result in less pain after surgery.
- Faster recovery: patients can return to normal activities much sooner compared to traditional surgery.
- Lower risk of complications: minimally invasive techniques reduce the risk of infections and other postoperative complications.
- Less visible scars: small incisions leave minimal scars, improving the aesthetic appearance.
Schedule your appointment
The Dr. Andrés MuñozA highly qualified neurosurgeon with outstanding training and experience in internationally renowned centers, specializing in Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery, offers personalized and advanced treatments for various spinal and cranial pathologies. Schedule your consultation today and take the first step towards a pain-free life!
For more information or to schedule an appointment, visit our website or call us directly.