Every everyday gesture, such as holding a cell phone, writing or peeling a fruit, can become annoying when the median nerve becomes trapped in the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the nerve is compressed inside the tunnel formed by the carpal bones and the transverse ligament, and its symptoms can seriously interfere with your daily life.
In this article you will discover a complete and useful guide about:
- Identify if you really have carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Understand what causes it and how it evolves.
- Know the most effective treatment options, including less invasive ones.
- Know how long it can last and what the actual recovery times are.
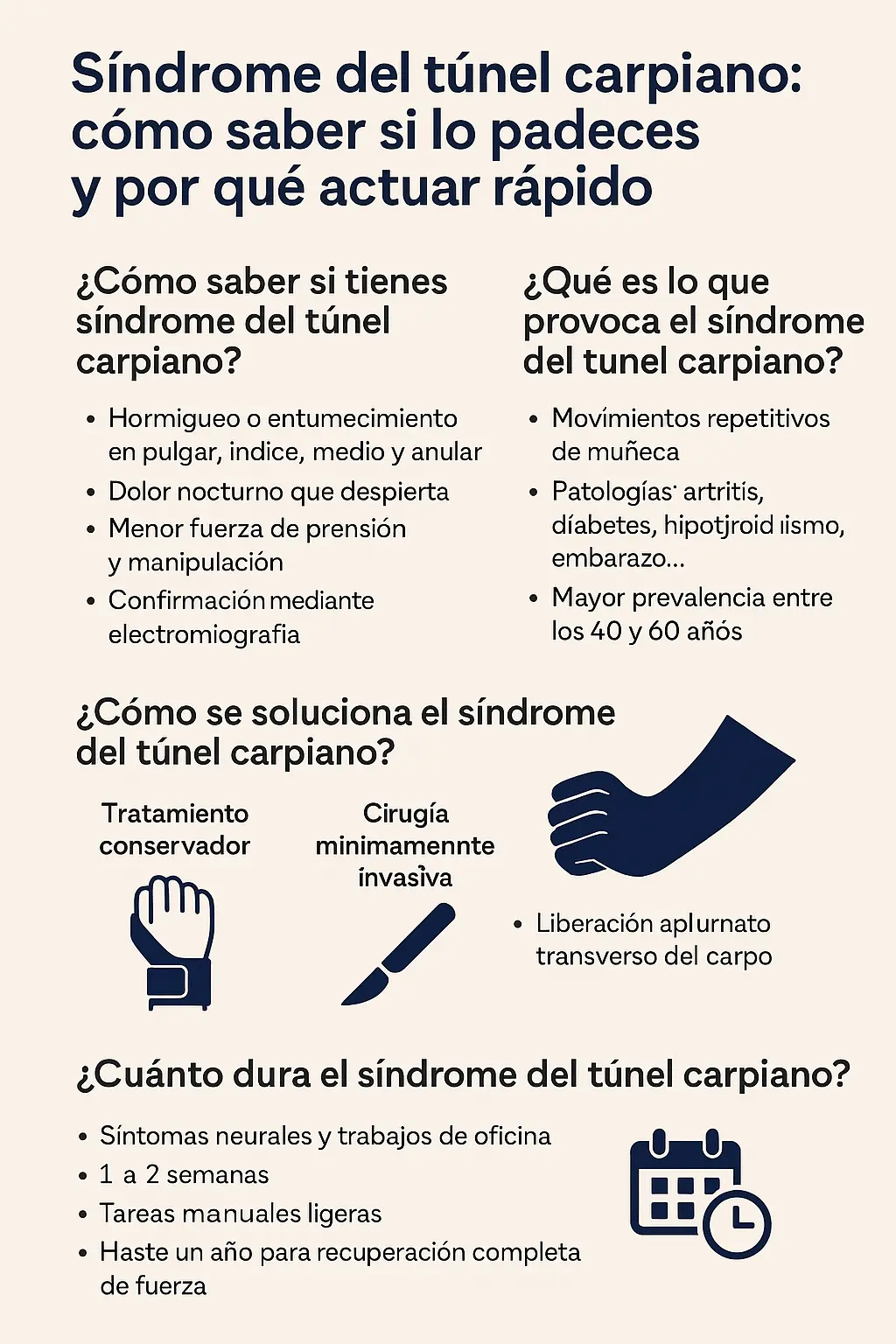
1. How do you know if you have carpal tunnel syndrome?
Diagnosis is based on a combination of characteristic symptoms and specific tests:
✔️ Frequent symptoms
- Tingling or numbness in thumb, index, middle or middle ring finger.
- Nocturnal pain that interrupts sleep.
- Feeling of weakness when grasping objects or writing.
- Pain that may radiate to the forearm.
✔️ Clinical tests
- Phalen’s test: keeping wrists flexed produces tingling in less than one minute.
- Durkan compression: direct pressure on the tunnel delays sensitivity with high diagnostic accuracy (~90%).
✔️ Electrodiagnostic confirmation
Electromyography (EMG) evaluates the conduction velocity of the median nerve and confirms the presence of nerve involvement.
2. What causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
The causes can be multiple, but the most common include:
🧠 Mechanical pressure on the median nerve:
- Narrowing of the tunnel due to ligamentous thickening, arthritis or fluid deposits.
- Repetitive use of the wrist in manual work, computing, vibrations or maintained postures.
🩺 Personal and systemic factors:
- Advanced age, obesity, diabetes, hypothyroidism or pregnancy.
- Inheriting an anatomically small carpal tunnel may further predispose to the problem.
It is one of the most common compressive neuropathies, with an estimated prevalence of 4-8% in people over 55 years of age and up to 14% in the general population.

3. How is carpal tunnel syndrome treated?
Treatment is scheduled according to the intensity of the symptoms and how it affects your life.
3.1 Conservative treatment (the first option)
- The use of night splints keeping the wrist in a neutral position reduces pressure and improves symptoms.
- Corticosteroid injections in the tunnel can relieve symptoms for a certain time in moderate cases. Adapt your environment: ergonomic keyboard, forearm support, frequent rest.
- Most respond well to these measures in 6 to 12 weeks, even in moderate cases.
3.2 Surgical treatment: decompression or carpal tunnel release
When the pain does not improve, there is progressive weakness, atrophy of the tenar eminence or persistent symptoms, surgery is recommended. This consists of sectioning the transverse ligament of the carpus, freeing the nerve, by means of a small incision in the palm of the hand at the level of the union with the wrist.
How long does carpal tunnel syndrome last?
⏳ Without surgery
Many people improve with conservative measures in a few weeks or months, although residual symptoms such as cramps or mild numbness may persist. Slow progression is not ruled out if the lifestyle is not adapted.
⏳ With surgery
- Initial recovery: neural symptoms usually diminish from the first few days.
- Return to office work: after 1-2 weeks.
- Light manual labor: 2 to 4 weeks.
- Maximum symptom improvement: between 6 and 10 months, with clinical stability after the sixth month.
- Full recovery of strength: may take up to one year.
In recent studies, 85% of patients achieved full functional recovery in about 3 months after prompt and well-indicated surgery.
How do you know if you need surgery?
Immediate consultation if:
- Numbness persists after 3 months.
- Visible weakness appears when grasping objects.
- Atrophy or loss of muscle mass is observed in the tenar eminence.
The decision must be personalized, always in collaboration between doctor and patient.
5. Frequently Asked Questions
Can carpal tunnel syndrome be disabling to work?
Yes, it has clear clinical evidence and limits ≥ 33% of your functionality can be recognized as disability.
Can it be completely reversed without surgery?
In most mild to moderate cases, yes. Conservative treatment well applied offers good recovery in 3 months with adequate follow-up.
What exercises are contraindicated?
- Avoid intense repetitive or vibratory movements.
- Do not put weight on the wrist or perform strenuous flexions.
- Do not lift more than 5 kg with the wrist involved during the acute phase.
Can carpal tunnel syndrome cause pain in the whole arm?
Yes, although the main focus of pain is usually in the wrist and hand, in advanced cases it can radiate to the forearm, and even to the elbow or shoulder. This pain is often accompanied by a dull, burning or heavy sensation. If not diagnosed in time, it can be confused with other pathologies such as cervical radiculopathy.
Can I have carpal tunnel in both hands?
Yes, in fact, it is estimated that between 30% and 60% of patients have bilateral involvement. It is more common in people with systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypothyroidism or rheumatoid arthritis. In these cases, the approach should be individualized, prioritizing the dominant hand or the most symptomatic hand for surgery if necessary.
How to distinguish carpal tunnel syndrome from tendinitis?
Both conditions affect the wrist and can be confused, but there are clear differences:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome mainly affects sensitivity (tingling, numbness) and sometimes strength.
- Tendinitis usually produces localized pain that increases with certain movements or with direct pressure on the tendons.
Phalen’s test or electromyography are key to differentiate both pathologies.
In summary, carpal tunnel syndrome is not a minor nuisance: it is a frequent condition, especially in women between 40 and 60 years of age, which can deteriorate the quality of life if not treated properly. Identifying it early, applying ergonomic solutions and starting conservative treatment can avoid surgery. But if symptoms persist or worsen, surgical release of the carpal tunnel, preferably using minimally invasive techniques, offers excellent success rates and functional recovery.
An early diagnosis, a specialized team and a personalized plan are your best allies to overcome this problem. Don’t wait for pain to limit your life: act now and recover the strength and sensation of your hands.
📍 Dr. Andrés Muñoz Núñez – Specialist in Neurosurgery and minimally invasive surgery techniques.
📞 609 688 469www.drandresmunoz.com
👉 Request your consultation here