The epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by an alteration in the electrical activity of one or more parts of the brain. and affects millions of people worldwide. For many, the control of seizures by medication ( anticonvulsants or anticonvulsants) can be a challenge, leading to a decrease in their quality of life. In such cases, in which it is difficult to control the disease with medication alone.medication alone, epilepsy epilepsy surgery emerges as a valuable option, offering real hope of reducing or even eliminating seizures.
In this article, we will explain what is involved in performing this type of intervention, when it is recommended, and what results can be obtained. In addition, we will discuss the diagnostic methods used to assess a patient’s suitability for surgery and the potential benefits and risks associated with it.
What is epilepsy surgery and when is it necessary?
The epilepsy surgery is a surgical procedure designed to remove or modify the part of the brain where seizures originate. This option is mainly considered for patients whose epilepsy is drug-resistant ( refractory epilepsy), a problem that approximately 25% of people with this condition.. The main objective of surgery is to improve the patient’s quality of life, since the reduction or elimination of seizures can mean a return to a fuller and more active life.
But, when should surgery be considered?
- Drug resistance: recommended when seizures are not adequately controlled with medications, despite trying various combinations and dosages.
- Impact on quality of life: if seizures significantly affect the patient’s ability to lead a normal life, surgery may be a viable option.
- Seizure location: if a specific area of the brain is identified that can be surgically intervened without causing damage to other neurological functions, surgery may be recommended.

Diagnostic methods: identifying the need for surgery
Before considering epilepsy epilepsy surgerysurgery, it is essential to make an accurate diagnosis to identify the brain area where the seizures originate and to determine whether surgical and determine if surgical intervention is feasible and safe.
Physical and neurological examination (usually performed by the clinician, in this case the Neurologist)
- Evaluation of reflexes, muscle strength and sensitivity: possible weaknesses or areas of numbness that may be related to the affected area in the brain are explored.
Specific diagnostic tests:
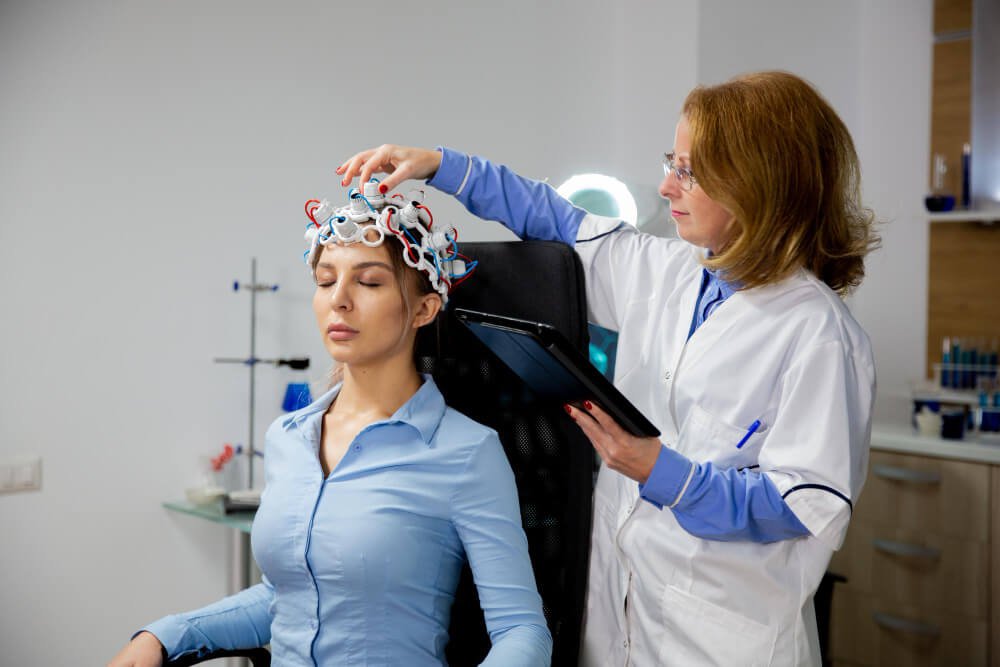
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): records the electrical activity of the brain to identify the areas where seizures originate. It is a fundamental test in the diagnosis of epilepsy.
- Video electroencephalogram (video EEG): combines EEG with continuous video of the patient to correlate seizures with alterations in brain activity. This is especially useful for confirming the diagnosis and localizing the epileptic zone.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): is the reference imaging testMRI provides detailed images of the brain, allowing the identification of structural abnormalities that may be associated with epileptic seizures. There are several types of lesions that can be seen on MRI in epileptic patients, such as cortical malformations, hippocampal sclerosis, tumors, and other types of lesions. etc. We can identify more and more lesions, even if they are subtle, due to the latest generation of MRI equipment.
- Prolonged EEG video: is a variant of Video EEG that is performed over a longer period, sometimes several days, to capture infrequently occurring seizures. This study is crucial for a thorough and accurate evaluation.
- Neuropsychological study: evaluates the impact of seizures on the patient’s cognitive and emotional function, helping to understand how surgery might affect these areas.
- Advanced neuroimaging tests: in addition to MRI, techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) or magnetoencephalography (MEG) can be used to precisely localize the epileptic focus and plan surgery more effectively. Even studies such as PET can be fused with MRI imaging.

Benefits of epilepsy surgery: improving quality of life
Opting for epilepsy epilepsy surgery can transform the lives of those suffering from frequent and debilitating seizures. Potential benefits of surgery include:
- Reduction or elimination of seizures: many patients experience a significant decrease in seizure frequency and intensity, allowing for greater control of their daily lives.
- Improved quality of life: the ability to perform daily activities without the constant fear of an impending crisis is one of the greatest benefits for those who undergo surgery.
- Reduced dependence on medication: in some cases, surgery makes it possible to reduce the dose of antiepileptic drugs or even eliminate them altogether.
Factors to consider before the intervention
As with any surgical intervention, it is essential that the patient and his or her family are well informed and understand all the implications before making a decision. For this reason, it is necessary to consider numerous factors such as the patient’s age (many patients are children), the family support they have when facing an intervention of these characteristics, their general state of health, etc. It is important to emphasize that the management of this disease should be multidisciplinary and preferably carried out in Epilepsy Units where specialists such as neurologists, neurosurgeons, neurophysiologists, neuropsychologists, etc. collaborate closely.
Types of interventions. Postoperative recovery. Expectations and long-term results.
There are many types of Epilepsy Surgery and, depending on the technique used, the recovery period may vary according to the nature or extent of the intervention. There is an enormous variability in the length of hospitalization, and the patient may have a short hospital stay, especially when the following are used minimally invasive techniques (lesions by radiofrequency, laser, etc.) or several days in the case of open surgery by means of craniotomy. craniotomy to remove one or more epileptogenic brain areas. However, rehabilitation and long-term follow-up are critical to ensure continued improvement and adaptation to any neurological changes that may arise.
What to expect after surgery?
- Regular neurological follow-up: Is essential to evaluate the effectiveness of surgery and adjust any additional treatment that may be necessary.
- Cognitive or physical rehabilitation: in some cases, may be necessary to help the patient recover functions that may have been affected during surgery.
- Surgery today offers high rates of probability of making seizures disappear (from 30% to 90%, depending on the type of epilepsy), with minimal percentages (slightly less than 1%) of generating serious superimposed lesions.

In conclusion, epilepsy epilepsy surgery is an option that can offer a significant improvement in quality of life for those who have been unable to control their seizures with medication. However, the decision to undergo this intervention should be based on a thorough evaluation by a medical team sufficiently trained in this type of pathology and a clear understanding of the benefits and risks involved.
Dr. Andrés Muñoz Núñez
Neurosurgeon
Málaga, Cádiz, Sevilla, Huelva
Phone: 951 749 631 / 609 688 469